学了2年Java,在北京根本收不到offer,面试官:IO流操作都不会
今日分享开始啦,请大家多多指教~
这篇文章给大家讲述了IO流,在java数据中所有数据都是使用流读写的。流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输。
一、前言
Java的I/O主要的用途就是文件数据的读写、数据的网络发送与接收等场合。
根据数据传输特性将流抽象为各种类,方便更直观地进行数据操作。对于文件内容的操作主要分为两大类分别是:字符流和字节流。
二、I/O流的分类
根据处理数据类型的不同分为:字符流和字节流。
根据数据流向不同分为:输入流和输出流。
1、字符流和字节流
字符流的由来: 因为数据编码的不同,而有了对字符进行高效操作的流对象。本质其实就是基于字节流读取时,去查了指定的码表。字节流和字符流的区别:
- 读写单位不同:字节流以字节(8bit)为单位,字符流以字符为单位,根据码表映射字符,一次可能读多个字节。
- 处理对象不同:字节流能处理所有类型的数据(如图片、avi等),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。
- 字节流在操作的时候本身是不会用到缓冲区的,是文件本身的直接操作的;而字符流在操作的时候下后是会用到缓冲区的,是通过缓冲区来操作文件,我们将在下面验证这一点。
结论:优先选用字节流。首先因为硬盘上的所有文件都是以字节的形式进行传输或者保存的,包括图片等内容。但是字符只是在内存中才会形成的,所以在开发中,字节流使用广泛。
2、输入流和输出流
对输入流只能进行读操作,对输出流只能进行写操作,程序中需要根据待传输数据的不同特性而使用不同的流。
三、代码实例
1、字节流读操作
package com.guor.javaSE;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IOTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test05();
}
private static final String const_filePath = "D:\\guor\\data\\test.txt";
private static final String const_filePathChinese = "D:\\guor\\data\\中文.txt";
private File const_file = null;
private File const_fileChinese = null;
public IOTest() {
this.const_file = new File(const_filePath);
this.const_fileChinese = new File(const_filePathChinese);
}
/**
* 字节流读取文件:单个字符读取
* @param b_chinese_file
*/
private static void test01(boolean b_chinese_file) {
IOTest ioTest = new IOTest();
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
if(true == b_chinese_file) {
//测试字节流读取中文乱码问题
fis = new FileInputStream(ioTest.const_fileChinese);
}else {
fis = new FileInputStream(ioTest.const_file);
}
int read = 0;
while ((read = fis.read())!=-1) {
log((char)read, false);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 字节流读取文件:数组循环读取
*/
private static byte[] test02() {
IOTest ioTest = new IOTest();
FileInputStream fis = null;
int len = 512;
byte[] buffer = new byte[len];
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(ioTest.const_file);
int read;
while ((read = fis.read(buffer,0,len)) != -1) {
log(buffer + "", true, false);
}
for(byte b : buffer) {
if(true == Character.isLetterOrDigit((char)b) || (char)b == "\n") {
log((char)b, false, false);
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
return new byte[1];
} catch (IOException e) {
return new byte[1];
} finally {
if(fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return buffer;
}
}
2、字符流读操作

3、字节流写操作
/**
* 字节流写操作
* @throws IOException
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
private static void test04() {
String outPath = "D:\\guor\\data\\testNew.txt";
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File file = new File(outPath);
byte[] buffer = test02();
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
log("FileNotFoundException: " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
log("IOException: " + e);
} finally {
if(fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}4、字符流写操作
/**
* 字符流写操作
* @throws IOException
* @throws FileNotFoundException
*/
private static void test05() {
String outPath = "D:\\guor\\data\\中文New.txt";
IOTest ioTest = new IOTest();
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader(ioTest.const_fileChinese);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int read = 0;
while ((read = fr.read()) != -1) {
log((char)read, false);
sb.append((char)read);
}
File file = new File(outPath);
fw = new FileWriter(file);
fw.write(sb.toString());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
log("FileNotFoundException: " + e);
} catch (IOException e) {
log("IOException: " + e);
} finally {
if(fw != null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5、log日志打印
/**
* @param msg 带输出信息
* @param b_wrap 是否换行
*/
private static void log(Object msg, boolean b_wrap) {
if(true == b_wrap) {
System.out.println(msg + "");
}else {
System.out.print(msg + "");
}
}
/**
* @param msg
*/
private static void log(Object msg) {
log(msg, true, true);
}
/**
* @param msg 带输出信息
* @param b_wrap 是否换行
* @param out 是否输出
*/
private static void log(Object msg, boolean b_wrap, boolean out) {
if(true == out) {
if(true == b_wrap) {
System.out.println(msg + "");
}else {
System.out.print(msg + "");
}
}
}四、多线程方式进行socket文件传送
socket通信时用socket.getOutputStream();获取输入输出流,不是socket通信时用new FileOutPutStream()获取输入输出流。
1、服务端
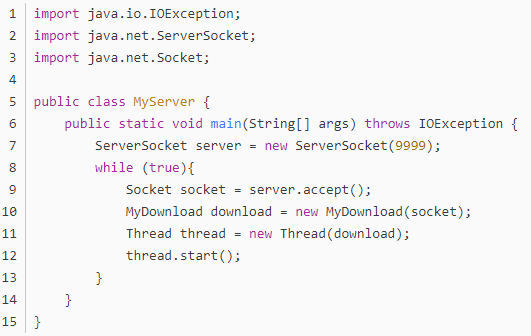
2、服务端Thread
public class MyDownload implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public MyDownload(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try{
System.out.println("与客户端连接成功");
//服务端向客户端发送消息
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
File file = new File("H:\\js\\jquery-2.1.4.min.js");
//将此文件从硬盘读到内存中
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
//定义每次发送的文件大小
byte[] bytes = new byte[1000];
int len = -1;
while ((len = in.read(bytes)) != -1){
out.write(bytes,0,len);
}
in.close();
out.close();
socket.close();
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}3、客户端
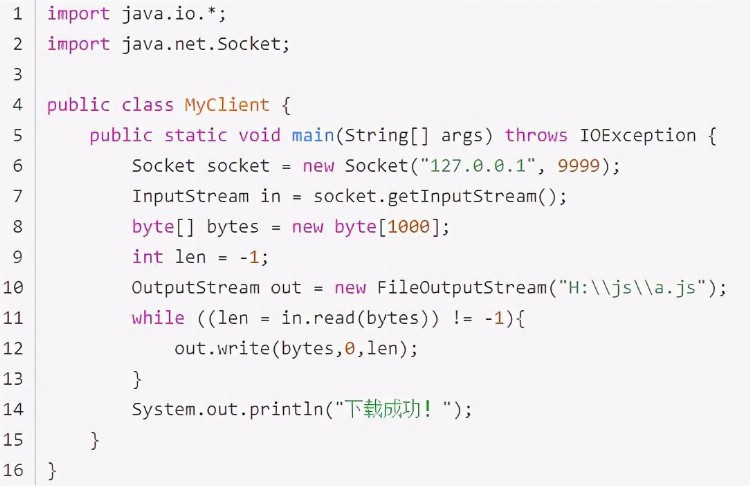
4、控制台输出
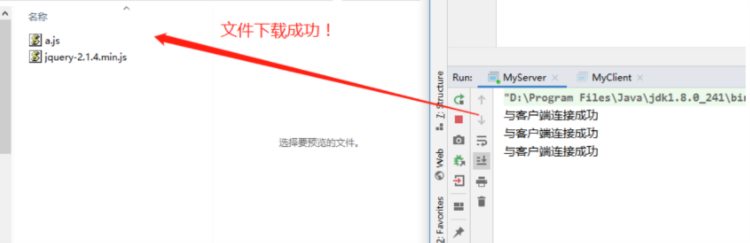
五、图片与byte数组互转
public class Image2ByteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "D:\\guor\\CSDN\\1.jpg";
byte[] image2byte = image2byte(path);
System.out.println(image2byte);
String path2 = "D:\\guor\\CSDN\\2.jpg";
byte2image(image2byte,path2);
}
// 图片到byte数组
public static byte[] image2byte(String path) {
byte[] data = null;
FileImageInputStream input = null;
try {
input = new FileImageInputStream(new File(path));
ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int numBytesRead = 0;
while ((numBytesRead = input.read(buf)) != -1) {
output.write(buf, 0, numBytesRead);
}
data = output.toByteArray();
output.close();
input.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex1) {
ex1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException ex1) {
ex1.printStackTrace();
}
return data;
}
// byte数组到图片
public static void byte2image(byte[] data, String path) {
if (data.length < 3 || path.equals(""))
return;
try {
FileImageOutputStream imageOutput = new FileImageOutputStream(new File(path));
imageOutput.write(data, 0, data.length);
imageOutput.close();
System.out.println("Make Picture success,Please find image in " + path);
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println("Exception: " + ex);
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
// byte数组到16进制字符串
public String byte2string(byte[] data) {
if (data == null || data.length <= 1)
return "0x";
if (data.length > 200000)
return "0x";
StringB